Definition Sheet
CHAPTER REVIEW QUESTIONS FOR QUIZ 1:
Instructions: Please e-mail your answers to miss.agro33@gmail.com or submit them in class Tuesday, March 29th!
You only have to answer: #1, 4, 5, 6, 8, and 9
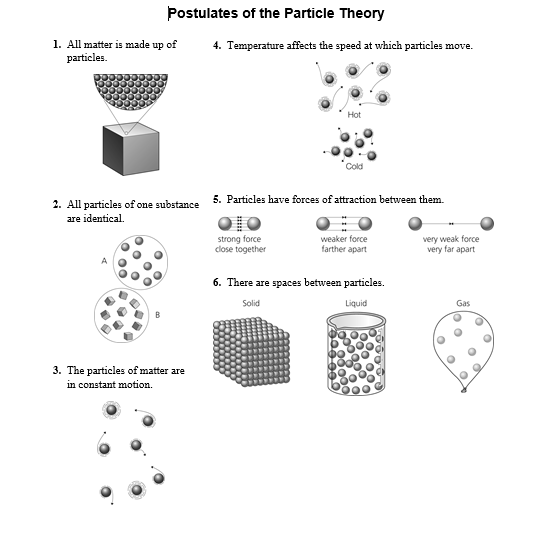
Your quiz is on Tuesday! Good Luck and Happy Studying! :)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Solubility, Concentration, and Saturation Note
Wednesday, March 29th
Name: _______________________
Separating Solutions and Mechanical
Mixtures
1) Solutions
can be separated by:
a)
______________________________ b)_______________________________
c) _______________________________
2) Mechanical
Mixtures can be separated by:
a)
______________________________ b)_______________________________
c)_______________________________ d)_______________________________
3)
In paper
chromatography, a highly _____________
_______________ is placed on a
single spot of paper and is absorbed. The distance that a substance moves
depends on its ________ in the solvent and its ____________ to
the paper.
4)
During evaporation,
water particles in a container leave the liquid (as ____________ ) and
mix with surrounding air particles. The escaping water particles have more _____________
and are moving ____________ than the remaining particles
5)
In an evaporating solution the __________________ of
the ______________ will increase because the number of solute particles
remains constant, while the number of solvent (water) particles decrease (turn
into vapour and evaporate)
6)
Distillation enables you to _____________
both the solute and solvent from a solution. During distillation, the solution
is _____________. This vaporizes the solvent (turning it into a gas) and
separates it from the solute. The solvent gas _________________, is
cooled, and is collected. This process is common when creating drinking water
from salt water. Distillation removes the __________ from the ___________ which
makes it drinkable!
7)
Filtration is the mechanical process of
separating ________ from ___________ or _________ using a porous
article or mass (For example, a paper filter being used to separate solid dirt
bits from a dirt and water mixture). When the mixture is poured into the
filter, the solid parts become ____________ in the filter, while the
water ________________ __________
the filter. Salt or other very small particles will pass through the filter and
remain in the water.
8)
When the components of a mechanical mixture are large and
easy to see, _____________ is a common form of separating (just like you
hopefully do at home with your Recycling Boxes!). Sorting is a technique involving separating materials based on
appearance (colour, size, texture). Sorting in recycling involves separating __________
from __________ and ________________ from _______________!
9)
Sifting is a means of separating
solids by component size. It involves shaking a ____________ material while it
passes through a screen or mesh. Components of the solid ________ enough to get
through the openings in the sifting device are separated from __________
components that cannot fit through the same openings. Sifting is very different
from ___________. Filters tend to have much ____________ holes than the
screens used for sifting so a solid that will pass through a screen will most
likely not pass through a filter. Also, filtration is used to separate solids
from liquids and gases, whereas sifting is used to separate __________
from other ____________.
10)
Some metals are magnetic because their particles are _____________
to the particles within magnets. ____________, _____________, and ____________ are
highly attracted to magnets, whereas most other substances are not. This form
of separation can separate car parts made with iron from parts like the tire,
dashboard, and foam insulation.
QUIZ #2 STUDY SHEET
YOU WILL ACE THE QUIZ IF YOU STUDY...
- The terms: concentration, evaporation, saturated, solute, solvent
- Examples of Solutions we have discussed in class (check out the orange powerpoint slides above)
- Factors Affecting Rate of Dissolving (powerpoint above)
- The concentration formula (make sure you remeber you have to divide the grams by the volume AND THEN multiply your answer by 100 to get the final answer of g/100mL
- Review the experiment we did in class (which solutes dissolved in which solvents?)
- The 7 ways to separate solutions and mechanical mixtures (powerpoint above)
Happy Studying :)
P.S. the 5 review questions above are due MONDAY (you may send them to miss.agro33@gmail.com or hand them in in class Monday)
YOU WILL ACE THE QUIZ IF YOU STUDY...
- The terms: concentration, evaporation, saturated, solute, solvent
- Examples of Solutions we have discussed in class (check out the orange powerpoint slides above)
- Factors Affecting Rate of Dissolving (powerpoint above)
- The concentration formula (make sure you remeber you have to divide the grams by the volume AND THEN multiply your answer by 100 to get the final answer of g/100mL
- Review the experiment we did in class (which solutes dissolved in which solvents?)
- The 7 ways to separate solutions and mechanical mixtures (powerpoint above)
Happy Studying :)
P.S. the 5 review questions above are due MONDAY (you may send them to miss.agro33@gmail.com or hand them in in class Monday)
Environmental/Separating Mixtures Fill-in-the-Blank Note
QUIZ #3 STUDY NOTES:
- Terms: paraffin wax, tailing ponds, percolation, leaching, cyanide, open pit mining, aeration, herbicide, landfill, radioactive, salt pan, sedimentation (and its part in purifying water),
- The Industrial Methods: Coal Mining, Sewage and Waste water Treatment, Pesticides, Landfills, Nuclear Energy, Refining Oil, Distillation, and their positive or negative effects on humans and the environment
- The types of pollution caused by each industrial separation method (radiation, air, water, or ground pollution)